Gallstone Pancreatitis: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Posted by Pankaj Dhiman on Feb 19th 2024
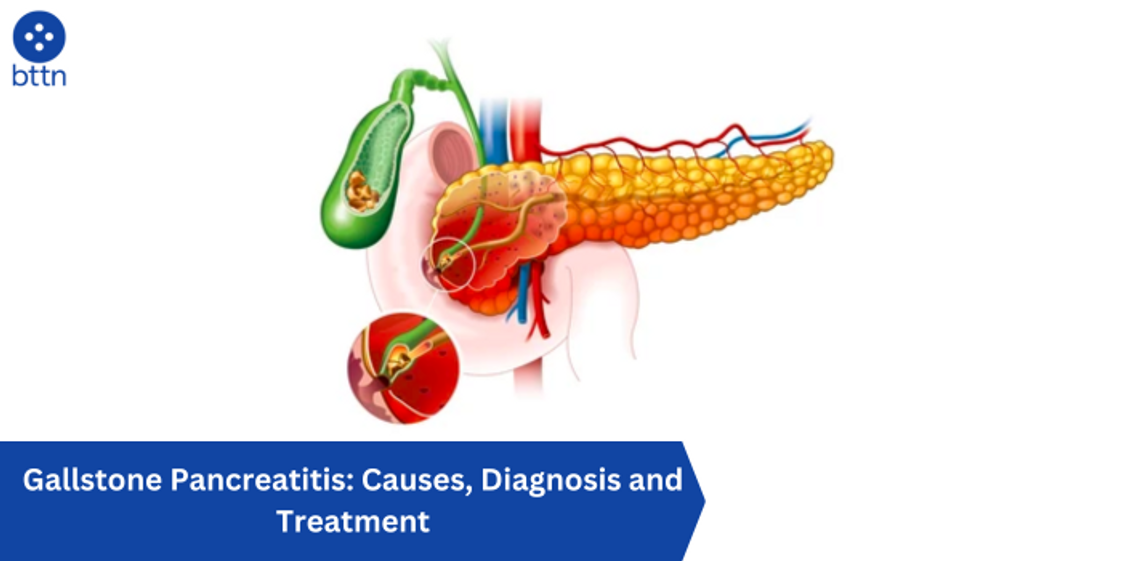
Gallstones, those hardened deposits in your gallbladder, can wreak havoc on your digestive system, and sometimes, even lead to a more serious condition called pancreatitis. Gallstone pancreatitis occurs when a gallstone lodges itself in the pancreatic duct, blocking the flow of digestive enzymes and causing inflammation in the pancreas. This inflammation can lead to intense pain, nausea, and other uncomfortable symptoms.
This blog delves deep into the world of gallstone pancreatitis, exploring its causes, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, potential complications, and preventive measures. Whether you're actively experiencing this condition or simply seeking information to stay informed, this comprehensive guide can provide valuable insights.
Let's dive into the details:
Gallstone Pancreatitis: Causes and Risk Factors
The primary culprit behind gallstone pancreatitis is, unsurprisingly, gallstones. However, certain factors can increase your risk of developing this condition:
- Female gender: Women are statistically more prone to gallstones and, consequently, gallstone pancreatitis.
- Family history: Having a family member with gallstones or pancreatitis makes you more susceptible.
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after 40.
- Obesity and overweight: Excess weight and body fat contribute to gallstone formation.
- High cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can solidify into gallstones.
- Diabetes: This condition can affect metabolism and increase gallstone risk.
- Rapid weight loss: Losing weight quickly can disrupt bile composition and promote gallstone formation.
- Certain medications: Some drugs, like oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy, might elevate gallstone risk.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Gallstone Pancreatitis
Gallstone pancreatitis often announces its presence through various symptoms, some common and others more severe:
Common Symptoms:
- Sudden, severe pain in the upper abdomen, radiating to the back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fever and chills
- Indigestion
Advanced Symptoms:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Rapid heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
- Confusion or mental disorientation
- Abdominal swelling
Diagnosing Gallstone Pancreatitis: Putting the Pieces Together
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Doctors typically employ a combination of approaches:
- Medical history and physical examination: Your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination to assess your symptoms and check for signs like tenderness or jaundice.
- Laboratory tests: Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes, indicating inflammation.
- Imaging studies: Abdominal ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs can visualize gallstones and locate any blockages in the pancreatic duct.
Treating Gallstone Pancreatitis: Addressing the Issue and Preventing Recurrence
The primary goal of treatment is to relieve pain, manage inflammation, and remove the obstructing gallstone. This may involve:
- Pain management: Medications like morphine can help alleviate pain.
- Intravenous fluids: Dehydration is a common concern, so fluids are administered to maintain hydration.
- Gallstone removal: This can be achieved through minimally invasive procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or, in some cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
Complications of Gallstone Pancreatitis: Understanding the Risks
In rare cases, gallstone pancreatitis can lead to serious complications, including:
- Infection
- Pancreatic necrosis (tissue death)
- Respiratory failure
- Kidney failure
- Shock
Proactive Management of Gallstones: Preventing Pancreatitis Before It Starts
If you have gallstones, taking preventive measures can reduce your risk of developing pancreatitis. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Exercising regularly
- Consulting your doctor about medication options to dissolve gallstones, if appropriate
Prevention is Key: Reducing Your Risk of Gallstone Pancreatitis
While some risk factors for gallstone pancreatitis are non-modifiable, adopting healthy lifestyle practices can significantly reduce your overall risk of developing gallstones and their associated complications.
Living with Gallstone Pancreatitis: Finding Support and Information
If you're facing gallstone pancreatitis, remember you're not alone. Numerous resources and support groups can offer guidance and connect you with others navigating similar experiences. Talking to your doctor and actively managing your health can help you overcome this condition and live a fulfilling life.
Remember: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment recommendations specific to your individual situation.